As the demand for renewable energy solutions continues to rise, off-grid solar systems have gained significant popularity among homeowners and environmentally conscious individuals. Harnessing the power of the sun to generate electricity, off-grid solar systems offer a reliable and sustainable alternative to traditional power sources. If you're considering embracing solar energy and going off-grid, this comprehensive guide will walk you through the process of designing and installing your DIY off-grid solar system.
I. Understanding Off-Grid Solar Systems: An Overview
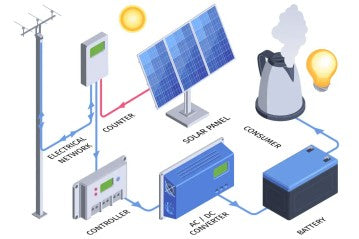
Before delving into the details of building your own off-grid solar system, it's crucial to understand the fundamental components and their functions. DIY Off-grid solar systems consist of three key elements:
1. Solar Panels: These photovoltaic (PV) panels convert sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity. The number of solar panels you require depends on your energy needs and the amount of sunlight available in your location.
2. Charge Controller: The charge controller regulates the flow of electricity from the solar panels to the batteries. It prevents overcharging and ensures optimal battery performance and longevity.
3. Batteries: Energy generated by solar panels is stored in deep-cycle batteries. These batteries provide a steady supply of power during periods of low sunlight or at night.
II. Designing Your Off-Grid Solar System: Steps to Success

1. Assess Your Energy Needs: Begin by calculating your average daily energy consumption. Consider appliances, lighting, and other electrical devices you use regularly. This assessment will help determine the size of your solar array and battery bank.
2. Determine Solar Panel Capacity: To determine the number of solar panels required, consider factors such as your location, available roof space, and the solar panel's wattage. For example, if you need 6,000 watt-hours of electricity per day and have 250-watt panels, you will need 24 panels (6,000 ÷ 250 = 24).
3. Choose the Right Battery Bank: Selecting the right battery bank is crucial for storing excess energy. Consider factors like battery capacity, voltage, and depth of discharge. Lead-acid and lithium-ion batteries are commonly used in off-grid solar systems, with lithium-ion batteries offering higher efficiency and longer lifespan.
4. Select a Charge Controller: The charge controller should match the voltage of your battery bank and the current output of your solar panels. PWM (Pulse-Width Modulation) and MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) charge controllers are commonly used. MPPT controllers are more efficient and can provide up to 30% more power.
5. Select an Inverter: An inverter is a critical component of your off-grid solar system as it converts the DC electricity stored in the batteries into AC electricity that can be used to power your appliances. There are two main types of inverters to consider:
a. Pure Sine Wave Inverters: Pure sine wave inverters produce a smooth and clean wave that closely mimics the electricity provided by the grid. They are ideal for powering sensitive electronics, such as laptops, televisions, and refrigerators. Pure sine wave inverters ensure compatibility with a wide range of appliances and reduce the risk of damage or performance issues.
b. Modified Sine Wave Inverters: Modified sine wave inverters are more affordable but produce a stepped waveform that may not be as smooth as utility power. While they can handle most basic appliances and power tools, some devices may not function optimally or may produce a buzzing sound. It's important to check the compatibility of your appliances with a modified sine wave inverter before making a choice.
III. Installing Your Off-Grid Solar System: Putting It All Together
1. Mounting Solar Panels: Ensure your solar panels are positioned to receive maximum sunlight exposure. You can choose between roof-mounted or ground-mounted systems. Roof mounting is common for residential installations, while ground mounting offers flexibility and easier maintenance.
2. Wiring and Connections: Proper wiring is essential for a safe and efficient off-grid solar system. Follow the manufacturer's instructions and local electrical codes when connecting solar panels, charge controllers, and batteries. Use appropriately sized wires and fuses to prevent overheating and electrical hazards.
3. Battery Bank Installation: Install the battery bank in a cool, well-ventilated area. Connect the batteries in series or parallel, depending on your system's voltage requirements. Ensure proper ventilation and secure the batteries to prevent accidents.
4. Connecting the Charge Controller: Connect the charge controller to the solar panels and the battery bank as per the manufacturer's instructions. Double-check the wiring to ensure correct polarity and tighten all connections securely.
5. Connecting the Inverter: Connect the inverter to the battery bank following the manufacturer's instructions. Ensure the inverter is grounded properly and the connections are secure. Double-check the polarity and wiring to prevent any electrical mishaps.
Conclusion
By understanding the components, designing, and installing your own off-grid solar system, you can take a significant step towards energy independence and reduce your carbon footprint. Remember to conduct thorough research, adhere to safety guidelines, and consult professionals if needed. DIY off-grid solar systems offer a rewarding experience, enabling you to generate clean, renewable energy and pave the way for a sustainable future.
Embrace the power of the sun and unlock the potential of off-grid solar systems to meet your energy needs efficiently and sustainably.

0 Kommentare